APA headings (6th edition) | How to use and format (example)
A paper is usually divided into chapters and subsections. Each chapter or section has its own heading, and these headings provide structure to a document. As well as many other APA format requirements, there are specific guidelines for formatting headings to ensure that all papers are uniform and easy to read.
APA heading formatting
The APA formatting guidelines for each heading style are outlined in the table below. APA recommends using 12pt. Times New Roman font for both the body text as the headings.
| Heading 1 | Centered, Bold, Title Case Capitalization* |
| Heading 2 | Left-Aligned, Bold, Title Case Capitalization* |
| Heading 3 | Indented, bold, sentence case capitalization,** a final period. The body text begins immediately after the period. |
| Heading 4 | Indented, bold, italics, sentence case capitalization,** a final period. The body text begins immediately after the period. |
| Heading 5 | Indented, italics, sentence case capitalization,** a final period. The body text begins immediately after the point. |
* Capitalize the first word of the title and all major words (including words that have four or more letters). Example: The Effects of Autism on Listening Skills.
** Capitalize the first word of the title and proper nouns (just as you would capitalize a sentence). An example: Teenagers with autism in the United States.
APA headings example
The example shows the different heading levels according to APA style. Hover over the different headings to see the specific APA formatting guidelines. You can also download the APA heading Template to add the correctly formatted APA heading styles to Word.
Download APA Headings Template
The Effects of Smartphones on the Attention in Classrooms
Method
This research aims to gain insight into the relationship between smartphones and students’ attention in classrooms. This chapter further discusses the research method, the sampling method and the data analysis procedure.
Research Method
In addition to an extensive literature review, 40 interviews were conducted for this study. The goal of conducting interviews was to find out how students looked at the use of smartphones in the classroom.
Sampling Method
A non-probability sample was used to gather participants for this research. The driving factors behind this decision were cost and convenience.
Procedure. Participants were given an introductory text prior to the survey. In this introductory text, the participants were informed that all answers would be processed anonymously.
Participant recruitment. Students who participated in this study were recruited through posts on the school’s Facebook page. As an incentive, students who participated were granted an exemption for writing an essay.
Participant assessment. Participants were selected based on their age and gender to acquire a representative sample of the population. Furthermore, students had to share additional demographic information.
Data Analysis
The interviews collected for this research were transcribed and then coded. Next, the coded interviews were analysed and compared. The statistical program SPSS was used to perform the analysis.
Results
First Hypothesis
The first hypothesis was tested using a regression analysis that used attention in classrooms as the dependent variable and the use of smartphones as the independent variable. The results of this analysis showed that the attention of the student decreases when a smartphone is used.
Using heading levels
Using the right heading levels not only helps readers navigate your paper, but also enables you to automatically generate an APA style table of contents in Word.
Use as many heading levels as you need. Some papers only have three heading levels, whereas others use all five. It’s also possible for one section (e.g. “methods”) to have more subheadings than other sections. When writing your paper or thesis, you will often use these heading levels:
Heading 1: Use heading 1 for the main elements of your paper, such as the “methods,” “results,” “conclusion” and “discussion” sections.
Heading 2: Use heading 2 for the subsections underneath heading 1. For example, under “methods,” include sections describing the “participant selection,” “experiment design’ and “procedure.”
Heading 3: The heading 2 subsections (e.g. “procedure”) can be split up further into subsections such as “data collection” and “data processing.” Use heading 3 for these subsections.
Heading 4 and 5: Depending on your paper, you can also use heading 4 and 5 for subsections that fall underneath heading 3 and 4, respectively.
Aligning Word’s heading styles to APA style
Instead of formatting every heading individually, use Word’s built-in headings feature, which you can find in the toolbar at the top of your document. This is the easiest and fastest way to format all the headings in your paper.
By default, Word’s heading styles do not follow APA style. However, you can change the default settings by right-clicking on the heading style and selecting “modify.”
You can also download the Scribbr APA Heading Word template. When attaching this template to your Word document the correctly formatted APA headings are added and the heading formatting will automatically apply on all existing headings.
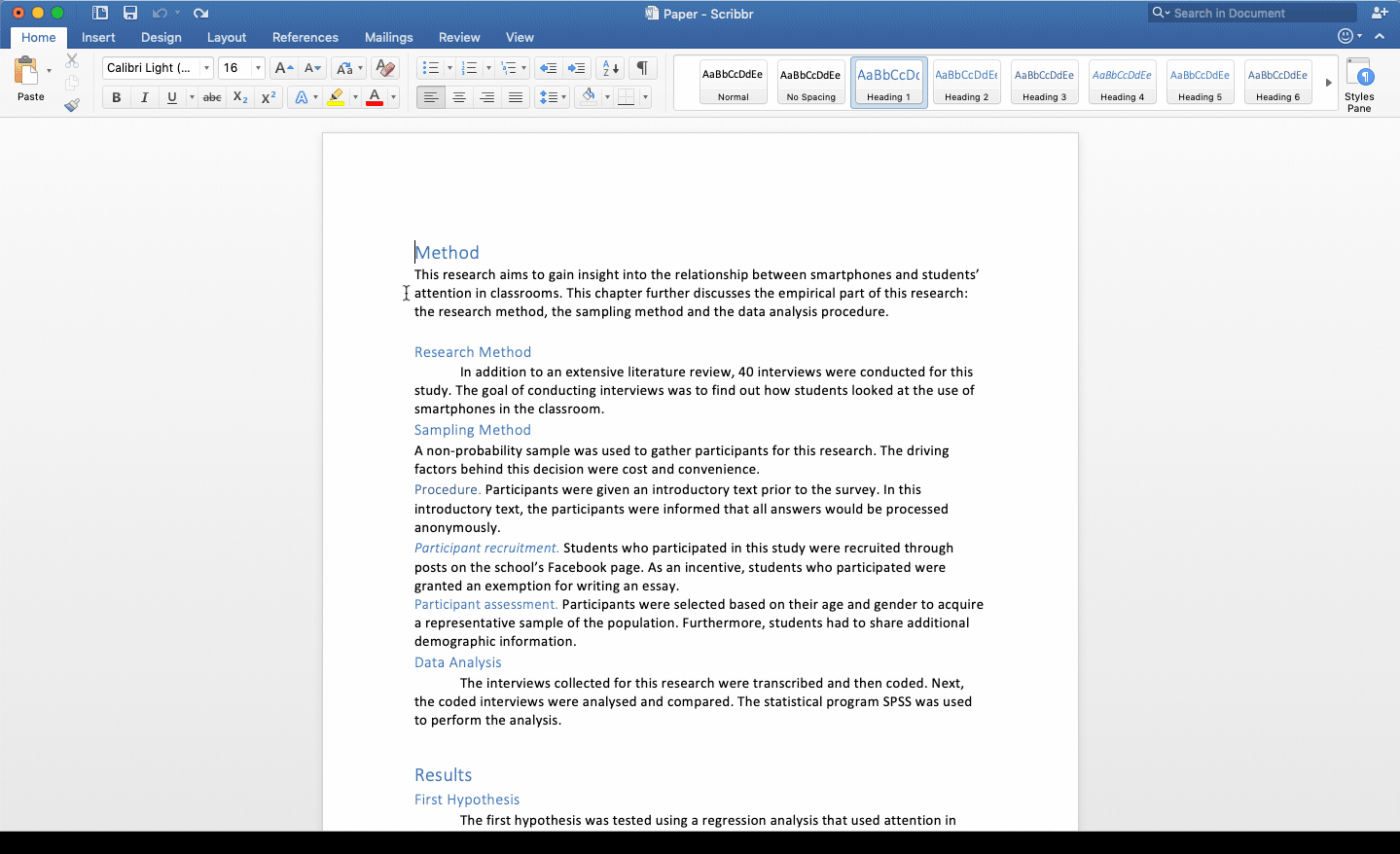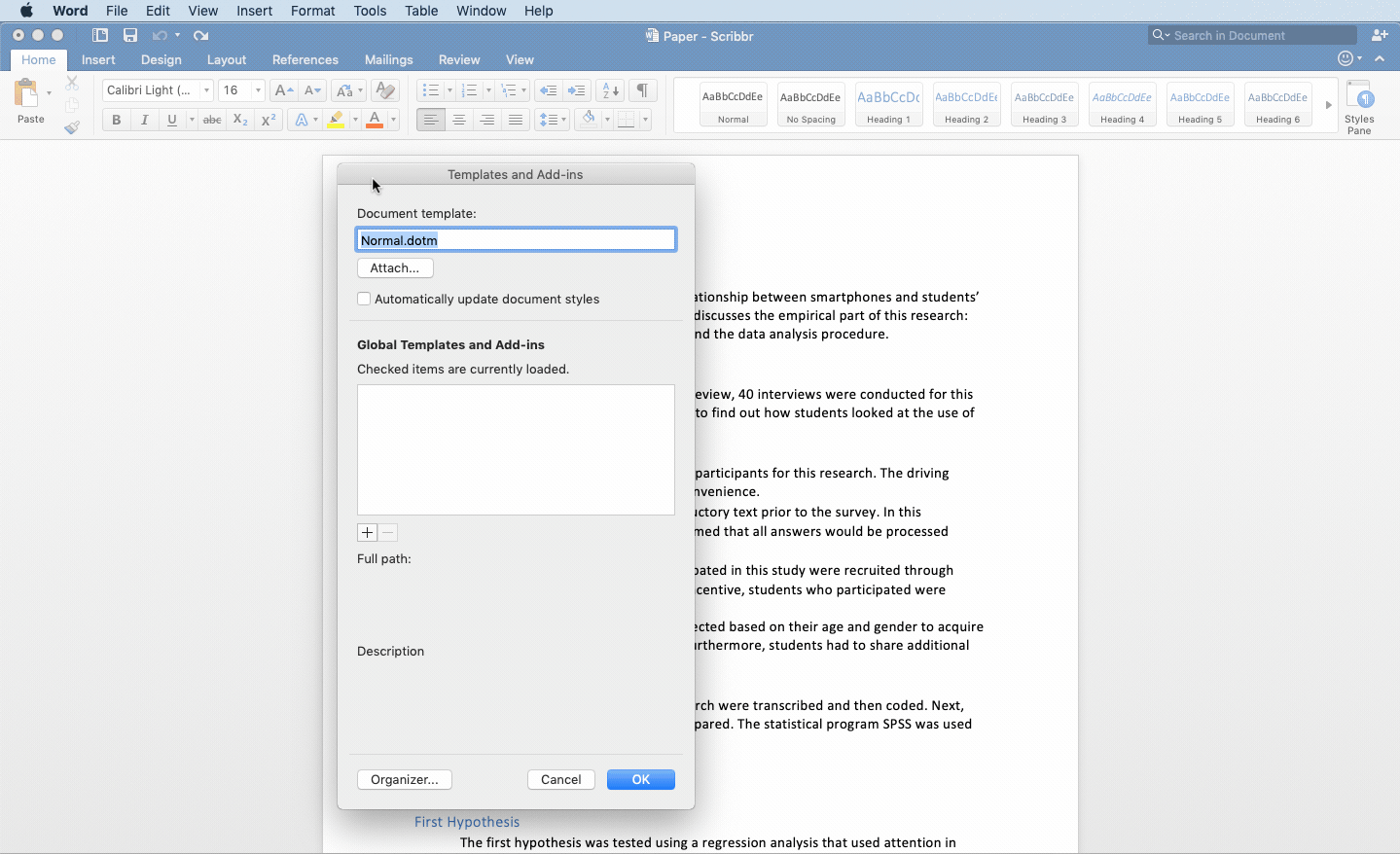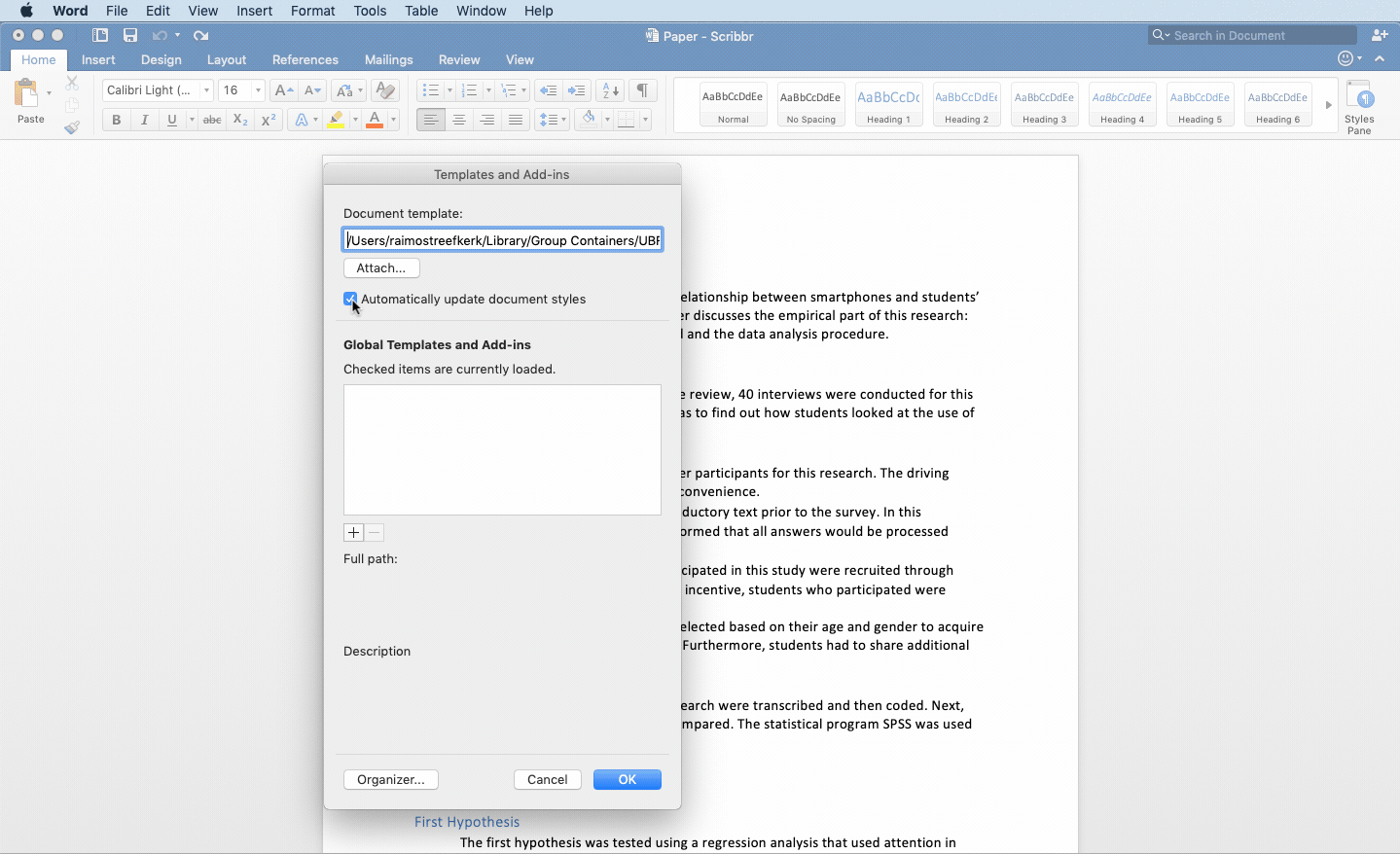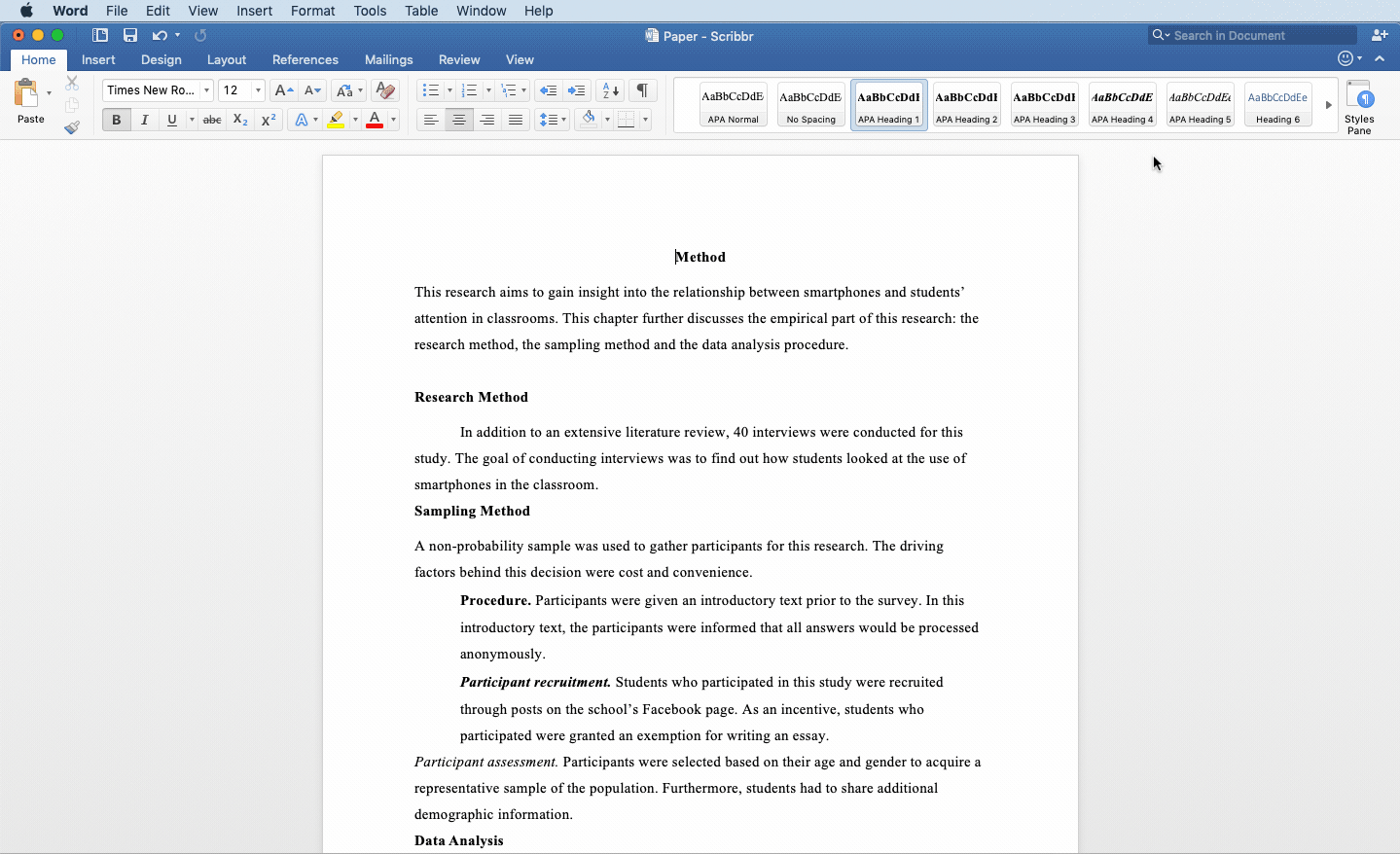
To attach the APA heading template to your Word document go ‘tools’ and ‘Templates and Add-ins’. Next, attach the downloaded template to the document and check the box ‘automatically update heading styles’.
Setting up in Google Docs
This video will demonstrate how to format different APA heading levels in Google Docs.
Sources in this article
We strongly encourage students to use sources in their work. You can cite our article (APA Style) or take a deep dive into the articles below.
This Scribbr articleStreefkerk, R. (November 7, 2020). APA headings (6th edition) | How to use and format (example). Scribbr. Retrieved October 17, 2022, from https://www.scribbr.com/apa-style/6th-edition/archived-headings/